Although there isn’t a conclusive measurement type or chart for body fat or the ‘healthy’ range for body fat, there are two different charts that provide a common understanding into the subject and what can be classified as healthy or unhealthy levels.
For individuals aiming to lose weight, understanding what the average body fat percentage is can aid in devising a useful training and fitness method to achieve their aim.
The body fat percentage charts provided can help you to understand what level of exercise and dieting is necessary for weight loss or weight gain. More recently, there are body fat scales that make it easier to measure body fat without leaving the home.
ACE body fat chart
The ACE body fat chart (American Council on Exercise) is the most commonly used table in gyms and other sports institution when instructing in regards to the ranges of body fat and is tied very closely to a person’s BMI (body mass index).
Whereas a person’s body mass index calculation provides an overview of a suggested healthy weight range in relation to their height overall, the body fat percentage chart focuses more on the levels of fat stored in the body. As shown in the official table below women generally have a significantly higher percentage of body fat compared to men.
| Description | Women | Men |
|---|---|---|
| Essential Fat | 10-13% | 2-5% |
| Athletes | 14-20% | 6-13% |
| Fitness | 21-24% | 14-17% |
| Acceptable | 25-31% | 18-24% |
| Obesity | >32% | >25% |
Body Fat Percentage %: Classification by ACE
The needs of women are taken into consideration in the above chart as more fat reserves are required. Women usually carry a slightly higher level of body fat than men due to their physical and hormonal differences e.g. lower muscle definition, ovulation and general body composition.
Essential Fat
This is the lowest limit of the scale and describes the range for the essential portion of fat in the body. This relates to a body fat percentage that is the minimum requirement needed for the body to operate functionally with a very high lean muscle mass.
It is below the ‘healthy’ or ‘fit’ range as having a body fat percentage this low can be owed to an extremely healthy or very unhealthy lifestyle.
Athletes/Fitness
This section of the table indicates the ideal range for sports professionals or fit individuals, this would be the range most recommended for sports such as basketball, football, tennis, and cricket.
At this level, the individual is likely to have lean muscle mass and also has enough fat stores to replenish energy from rigorous training, but not too much to affect their cardiovascular health.
Acceptable
The common range for the average man or woman, this encompasses those who do not necessarily exercise often or are involved in sports, but whose body fat percentage does not to put them at risk of associated illnesses.
It is essential that those in this range ensure they do not adopt poor nutritional habits and at least add more exercise into their lifestyle routines. This reduces the risk of the body fat increasing to dangerous levels.
Obesity
Those in this range would typically be classified as obese or morbidly obese, it is usually advised at this stage to contemplate a safe weight loss regime. The ACE table indicates that body fat values at this level suggest too much visceral and subcutaneous fat which increases the chance of related diseases and cardiovascular problems.
Some arguments in relation to this body fat measurement table refer to the fact that various sporting and performance needs are relative to what is required.
For example, a bodybuilder boasting a body fat value around 5% (for men) or 10% (for women) would be at the height of fitness and performance, whereas a person who has the same percentage due to malnutrition or drug abuse will be at a totally different end of the scale in terms of health and well-being.
Likewise, a sumo wrestler will possess a high body fat percentage but is likely to have very good blood lipid levels and long life expectancy.
Jackson & Pollock Caliper Chart
The caliper is one of the most accurate “everyday use” methods to best measure body fat, the best known being the Accu-Measure body fat caliper.
Together with researchers Jackson & Pollock, a chart was created to more accurately define the “ideal” body fat ranges on both men and women, based on the caliper measurement results.
The research of Jackson & Pollock in the field of body fat measurement has long become the de-facto industry standard for the skin-fold measurement.
The measurement with the Caliper is straightforward: At various points of your body, you can measure the thickness of your skin fold and then calculate the sum of all readings to get a percentage. The body fat measurement calculators can then be used for measurements to understand exactly where you are positioned in the chart based off the readings.
The tables may seem complex at first glance, in fact, they are quite easy to read and understand.
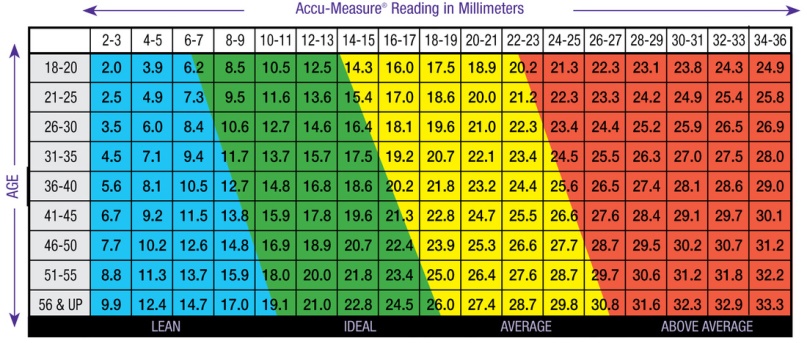
Body Fat Percentage Measurement Chart for Men
Body Fat Percentage Measurement Chart for Women
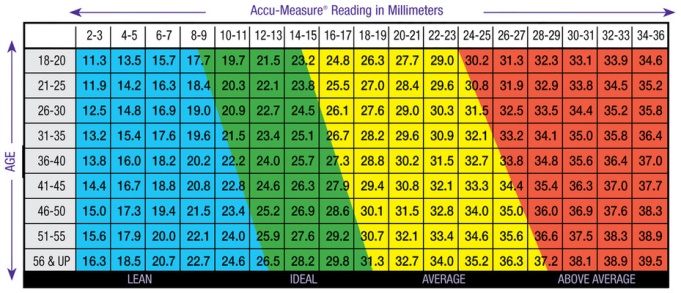
- Skinfold thickness (in millimetres): the headings of the columns show various values for the ‘pinch’ test with the caliper. You can find the value required by adding all the measured skinfold thicknesses (“Accu-Measure Reading in millimeter”)
- Age: the leftmost column displays the classification by lines of young (first row) to oldest (last line)
- Body Fat Percentage: this is the figure required from taking the test. It starts from 2.0% (top left) to 33.3% (bottom right) for men, and 11.3 to 39.5% for women.
- Colours: this provides the indication of the classification of a body fat percentage value. Slim (blue), perfect (green), acceptable (yellow) and overweight (red)
So for example a 35-year-old man with a body fat percentage of 13.7% would be seen as very ideal, lean and healthy, whereas another with a percentage of 26.3% may be seen as overweight and in need of a lifestyle change to reduce the amount of fat in their system, which leads to the process of weight loss.
The body changes with age and usually stores more fat as we get older. This is because the body stores fat in different ways.
- Subcutaneous fatty tissue: (subcutaneous fat) fat that is stored just under the skin
- Visceral fat: fat that our internal organs, especially the digestive tract of our sheathed.
- Building and muscle fat: Serves mechanical protection (e.g. on sole, joints) or is incorporated directly in the muscle
Out of these three types the subcutaneous fatty tissue affects how the skins looks and feels. As we age, the proportion of the other two types of body fat increases naturally.
When an individual aims to lose weight, they are aiming to shed the visceral fat, which can be dangerous to the body and long term health if at a high level.
Body fat does provide some insulation therefore it is also important to ensure that an individual does not go to extreme lengths just to lose weight, as this can also be bad for a person’s health.
What is the ideal body fat percentage?
The ratio between fat-lean is different for various reasons, making it harder to provide an exact percentage that is ideal for everyone. In general, it is suggested that the average healthy body fat range should be 15-20% in men and 20-25% in women (due to their varying body compositions).
Athletes and sports professionals on the other hand (depending on the sport) will be required to be at the lower end of the fat percentage chart, due to the requirement of lean weight (muscle mass).
While such low levels may seem great for the body composition, it does not guarantee great sporting success in the long term as other factors come into play.
Body Fat Percentage % for Athletes
| Sport | Men | Women |
|---|---|---|
| Football | 10-18% | 13-18% |
| Basketball | 6-12% | 20-27% |
| Swimming | 9-12% | 14-24% |
| Volleyball | 11-14% | 16-25% |
| Cycling | 5-15% | 15-20% |
| Hockey | 8-15% | 12-18% |
| Tennis | 12-16% | 16-24% |
| Long distance running | 5-11% | 10-15% |
| Rugby | 10-13% | 13-16% |
| Gymnastics | 5-12% | 10-16% |
Even when under 8% and women under 14% are not said to be at a particularly high health risk, extremely low body fat though is an issue and could pose serious health risks.
The body requires a certain level of fat to function properly, so apart from the ‘essential’ body fat needed for the body’s organs to function, it is therefore normal and recommended to have a certain level of ‘storage’ fat also to protect these organs and prevent any long term health problems.
SOURCE
- Jackson AS1, Pollock ML. (1978) Generalized equations for predicting body density of men
- Body Composition Information and FAQ’s Sheet
- Jeukendrup, Asker and Michael Gleeson. Sport Nutrition – An Introduction To Energy Production And Performance. 2nd ed. 2010. Print.[/trx_infobox